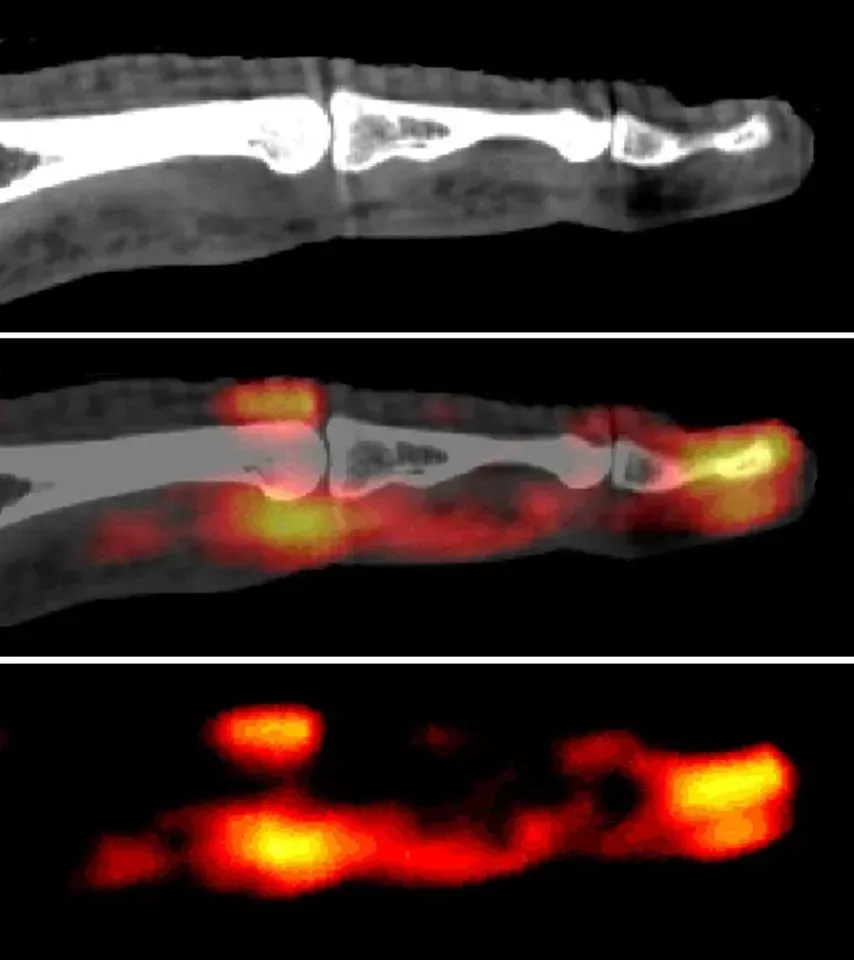
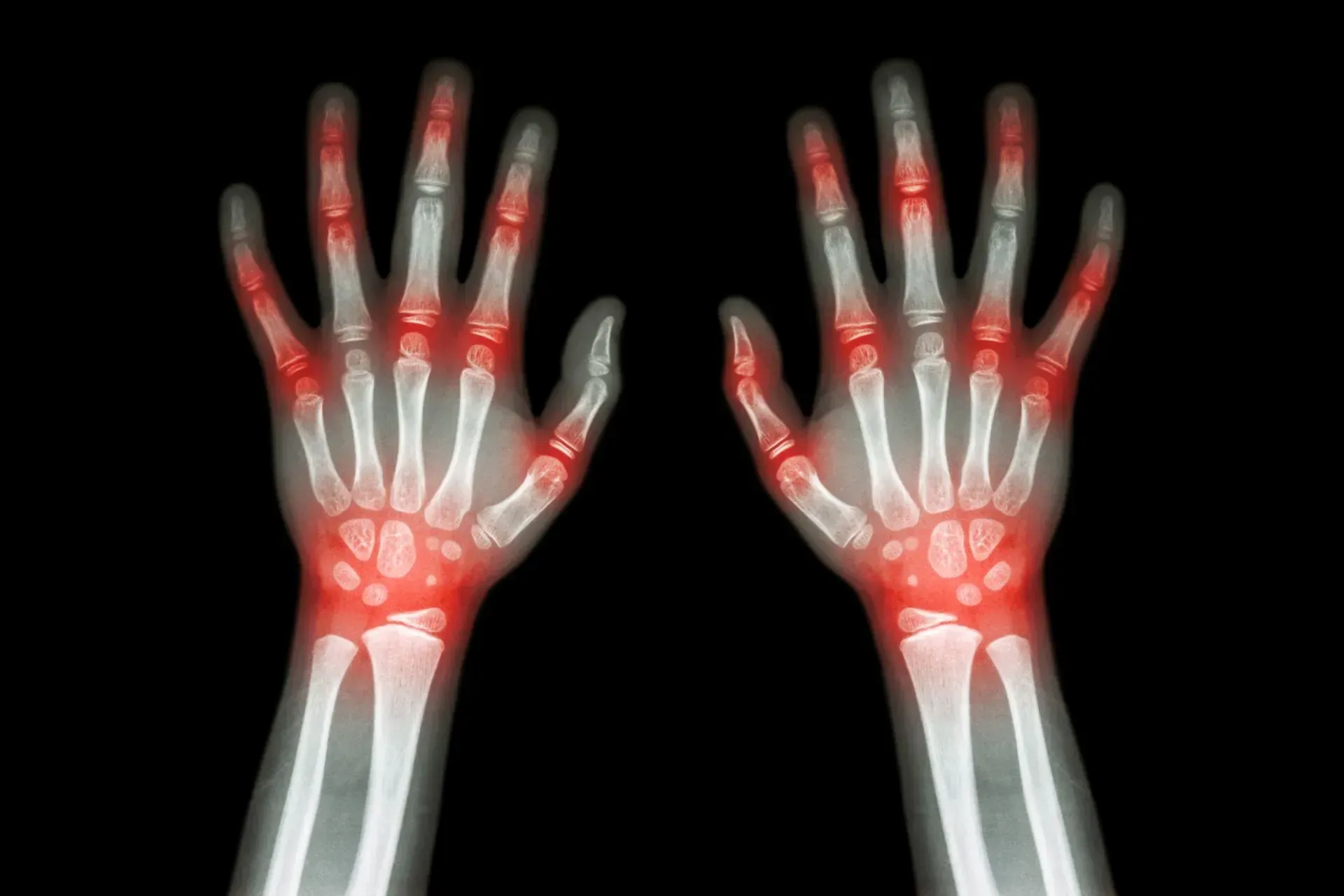
Rheumatoid Arthritis
How to pronounce it: Rheumatoid - roo·muh·toyd
AiArthritis defines Rheumatoid Arthritis as:
Rheumatoid arthritis (RA) is a chronic inflammatory condition that can affect your joints, tissues, and organs. RA is an autoimmune disease where the immune system mistakenly attacks healthy tissue.
Symptoms & Characteristics
Common in All AiArthritis Diseases
Flares: Periods of worsening symptoms are called flares. A flare can last for hours, days, weeks, or months.
Physical Activity: Condition improves with activity and exercise and worsens with rest.
Comorbidities: When inflammation is left uncontrolled due to lack of proper treatment, comorbidities can develop. 70% of patients with chronic, lifelong disease will develop comorbidities, including dual or triple diagnoses.
Family History:
Autoimmune diseases often run in families, indicating a potential genetic predisposition where that gene can cause disease. Autoinflammatory diseases can occur multiple times in a family, but is based off of genetic mutation. It is not a gene that causes the disease— but a mutation on the gene that can cause the disease which can then be passed on to the next generation.
"Auto" Symptoms
Fatigue: Severe fatigue or exhaustion that may not be helped by caffeine/stimulants and can happen even after a long period of rest.
Cognitive Dysfunction: Brain fog or periods of time where thinking gets clouded and it becomes difficult to concentrate.
Flu-like symptoms: Without having the flu- nausea, muscle weakness, and general malaise.
Fever: Typically low grade in autoimmune (with exception of juvenile idiopathic arthritis) and higher grade in autoinflammatory (% strongly varies per disease).
Reference: Early Symptoms of AiArthritis Study, AiArthritis, 2019.
Inflammatory Arthritis Symptoms
Stiffness: Severe stiffness in one or more joints, especially in the morning or after sitting for long periods of time.
Joint Pain: Episodes of joint pain that may last for hours, days, or even weeks, that can appear and disappear suddenly. Often described as “jumping pain” into different locations.
Typically the joint pain will coincide with one or more “Auto” symptoms and start and stop suddenly - for no apparent reason (which is called a "flare"). Some people will experience all of the above symptoms, others only a few.
If you have any of the arthritis features, and at least one of the “Auto” features, please consult your physician about a referral to a specialist.
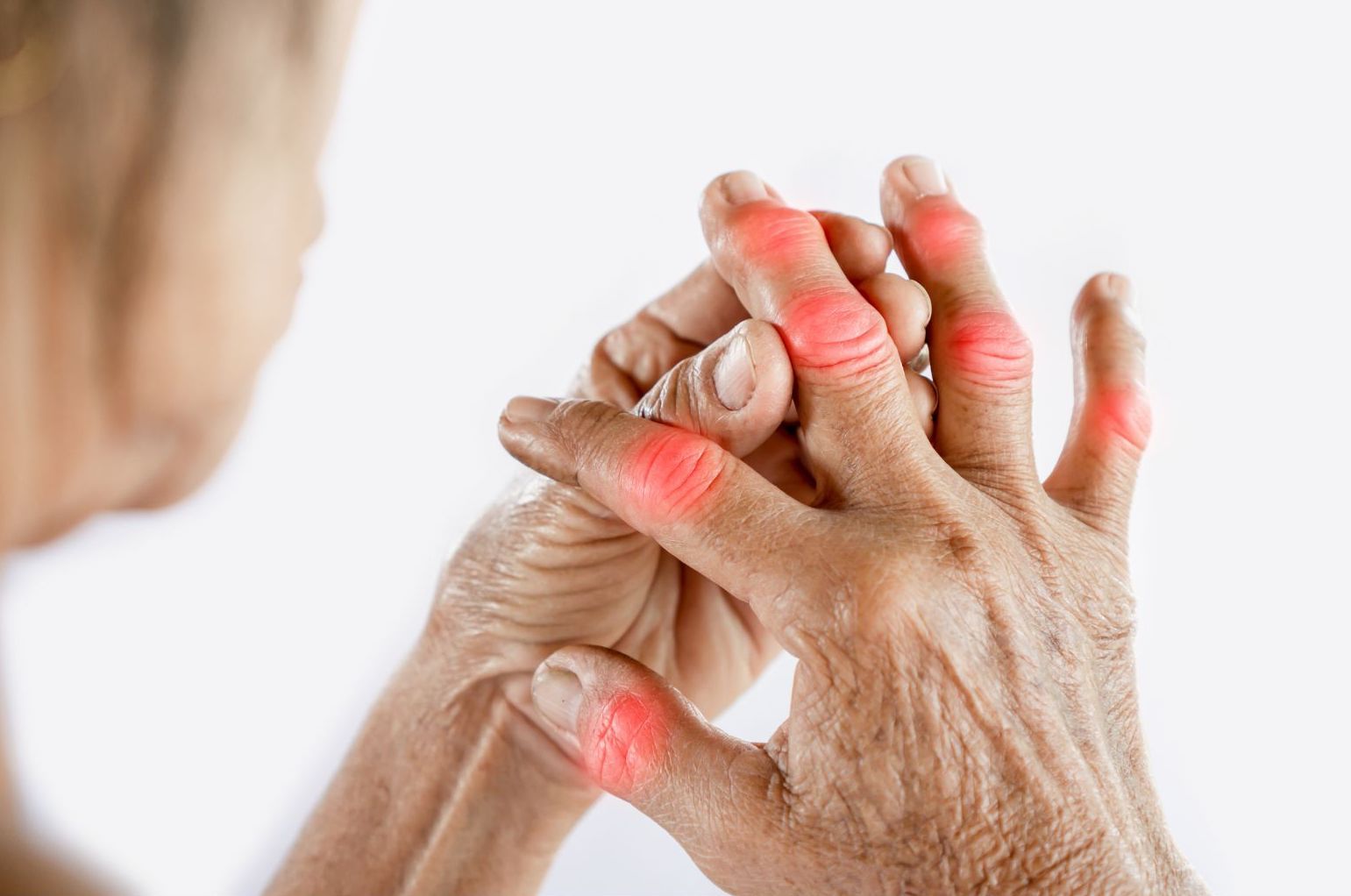
Symptoms Often Associated with Rheumatoid Arthritis
- Firm lumps under the skin, often around the elbows or hands
- Pain and swelling, usually affecting both sides of the body
- Redness and warmth around the joints
- Larger joints in the hands (like knuckles) are often affected first, but any joint can be involved
Diagnosing Rheumatoid Arthritis
Diagnosing rheumatoid arthritis (RA) involves a combination of physical exams, blood tests, imaging (such as MRIs), and family history. Doctors typically look for:
• More than one joint being affected
• Chronic symptoms lasting over 6 weeks
• Swelling, redness, or warmth in the joints (although these may not always be present)
• Other symptoms that help distinguish RA from osteoarthritis
Blood tests are important for diagnosing RA and may show markers of inflammation, such as ESR and CRP. A positive Rheumatoid Factor (RF+) is another common indicator, though it is not required for a diagnosis, as many people with RA do not have this marker in their blood. Similarly, anti-CCP (cyclic citrullinated peptide) antibodies are highly specific for RA and can help identify the disease early, even in patients who do not yet show symptoms. High levels of anti-CCP are often associated with more severe disease and a higher risk of joint damage.
Both RF and anti-CCP are part of the diagnostic and classification guidelines for RA. However, some patients may be negative for both markers, a condition referred to as seronegative RA. This means the absence of these specific antibodies does not rule out RA, and diagnosis may still be made based on symptoms, imaging, and other blood tests.
In addition to RF and anti-CCP, doctors may also test for 14-3-3eta, a protein released from joints during inflammation.1 This marker is specific to RA and can help identify the disease earlier, including in patients who test negative for RF and anti-CCP (seronegative RA).2,3 14-3-3eta is also valuable beyond diagnosis, since higher amounts are linked to a greater risk of joint damage and levels tend to fall when treatment is working.4,5 For this reason, it is often used together with CRP to monitor how well a treatment is controlling disease progression and to support ongoing care decisions.4,6
To further aid in diagnosis, doctors may use a points system developed by the
American College of Rheumatology (ACR) and the
European Alliance of Associations for Rheumatology (EULAR). This system assigns points based on test results and symptoms to help determine if you have rheumatoid arthritis.
References:
- Maksymowych WP, van der Heijde D, Allaart CF, et al. 14-3-3η is a novel mediator associated with the pathogenesis of rheumatoid arthritis and joint damage. Arthritis Res Ther. 2014;16(2).
- Maksymowych WP, Naides SJ, Bykerk V, et al. Serum 14-3-3η is a novel marker that complements current serological measurements to enhance detection of patients with rheumatoid arthritis. J Rheumatol. 2014;41(11):2104-2113.
- Naides SJ, Marotta A. 14-3-3η in “Seronegative” Rheumatoid Arthritis. J Rheumatol. 2015;42(10):1995.
- Carrier N, Marotta A, de Brum-Fernandes AJ, et al. Serum levels of 14-3-3η protein supplement C-reactive protein and rheumatoid arthritis-associated antibodies to predict clinical and radiographic outcomes in a prospective cohort of patients with recent-onset inflammatory polyarthritis. Arthritis Res Ther. 2016;18:3.
- Hirata S, Marotta A, Gui Y, Hanami K, Tanaka Y. Serum 14-3-3η level is associated with severity and clinical outcomes of rheumatoid arthritis, and its pretreatment level is predictive of DAS28 remission with tocilizumab. Arthritis Res Ther. 2015;17:280.
- Hirata S, Marotta A, Hanami K, et al. SAT0062: 14-3-3ETA predicts joint damage progression and flaring after adalimumab discontinuation. Annals of the Rheumatic Diseases. 2017;76:791.
More Information About Rheumatoid Arthritis
Rheumatoid Arthritis Treatment Options
Treatment OptionsTreatments are tailored to each individual's disease, but visit our Treatment Options page to learn more about the different types of treatments that are used for Rheumatoid Arthritis.
What Fellow Rheumatoid Arthritis Patients Want You to Know
Submit YOUR Advice- Sometimes you may feel a locking feeling in the joints, like if you grab a hair brush or a cabinet handle - suddenly your fingers may stop moving while the rest of your hand continues in motion. This doesn't feel good.
- Joints like your jaw can be affected. Also the vocal chords, called the cricoarytenoid joint (although this is not common)
- You CAN HAVE RA without positive blood work! You may hear some patients say they have "seronegative RA" or "seropositive RA". This is referring to their blood work. If a patient has "seronegative", it means they were diagnosed with RA and had no positive markers (inflammation, RF +, etc.) in their blood (normal bloodwork).
- A lot of patients choose not to use the word "arthritis" because they feel that's the only word others hear and think it's the same as the most common type of arthritis, osteoarthritis - caused by aging, wear and tear, overuse. While there has been movements in the past to try and change the name, there are many reasons why this is not likely to happen.
Interesting Facts about Rheumatoid Arthritis
- There used to be a diagnosis of Juvenile Rheumatoid Arthritis (JRA) decades ago, but after it was realized that juvenile arthritis onset is not exactly the same disease as RA, it was changed to Juvenile Idiopathic (no known cause) Arthritis, or JIA. You may still hear people refer to it as JRA, especially if this was their diagnosis as a child.
- While some adults originally diagnosed with either JRA or JIA may refer to their current diagnosis as Rheumatoid Arthritis (RA), it's really a matter of choice. Some adults still say JRA/JIA OR will say JRA/JIA/RA.
- Evidence of RA-like symptoms has been found in skeletal remains of Native Americans dating back to at least 4500 B.C. This suggests that RA has been affecting humans for thousands of years. However, RA was not widely recognized in Europe until the 19th century.
- The term “rheumatoid arthritis” was coined in 1859 by British rheumatologist Alfred Baring Garrod. “Rheumatoid” comes from the Greek word “rheuma,” meaning “that which flows,” referring to the characteristic joint swelling.
Rheumatoid Arthritis Awareness Days/Months
- World Autoimmune and Autoinflammatory Arthritis Day - May 20th
- Rheumatoid Arthritis Awareness Day - February 2nd
- Autoimmune Awareness Month - March
- Arthritis Awareness Week (UK) - May
- Arthritis Awareness Month (US) - May
- Arthritis Awareness Month (Canada) - September
- World Arthritis Day - October 12th
- Rheumatic Disease Awareness Month - September
- Pain Awareness Month - September
- Chronic Disease Awareness Day - July 10th
- Invisible Disabilities Week - 3rd full week of October
Other Rheumatoid Arthritis Resources
Share Your Story & Get Involved!
Sometimes the best medicine is diving in to learn more, meeting those who have similar lived experiences, and doing activities that can help to improve your health and the
AiArthritis community!

Where to Start:
- Follow
AiArthritis on Social Media:
- Become a Volunteer
- Join AiArthritis Voices
- Submit a Rant
- Join our Research Database
- Join our Online Community
Share Your Story:
Being a mystery patient and seeking a diagnosis can a tough, lonely, and frustrating journey. Your story is unique and can potentially help us to help other patients. What would you want fellow patients to know about YOUR diagnosis journey ? Your patient-identified issues can aid us in creating patient-infused solutions.